ThingsKit
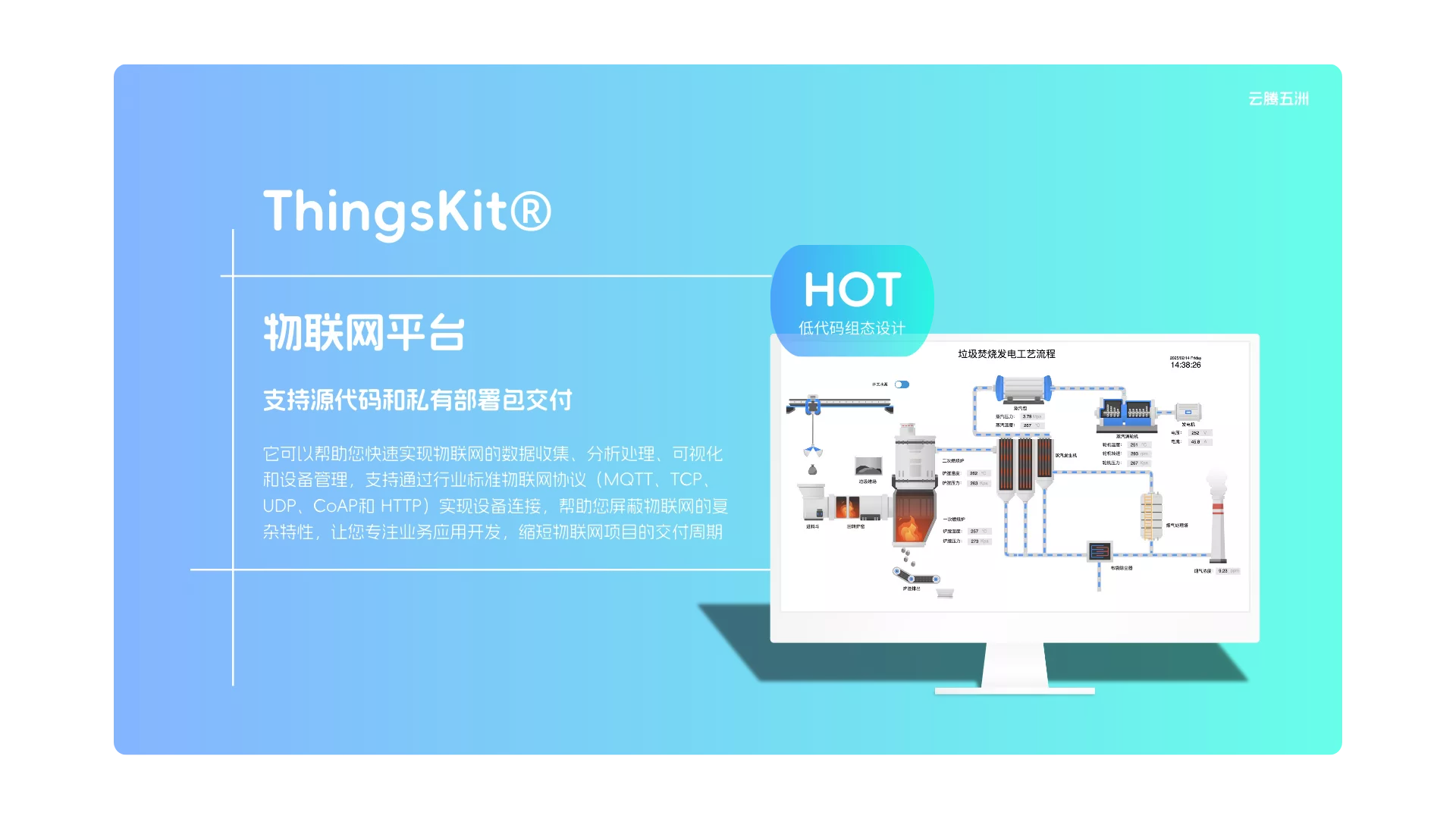
物联网平台
物联网平台能将各种传感器、摄像头、生产设备和系统连接到企业私有云,实现数据的采集、传输、处理和应用。帮助您屏蔽智能物联网的复杂特性,让您专注业务应用开发,缩短物联网项目的交付周期。
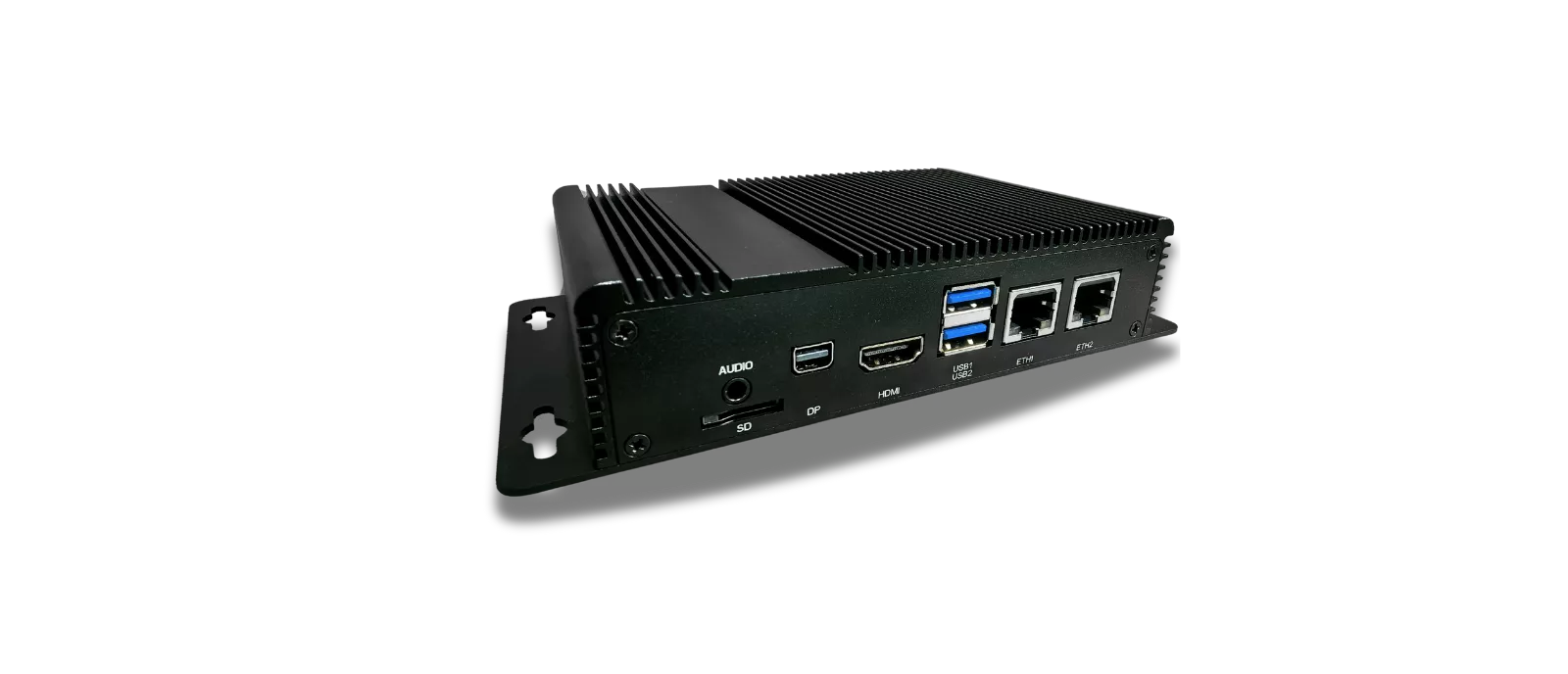
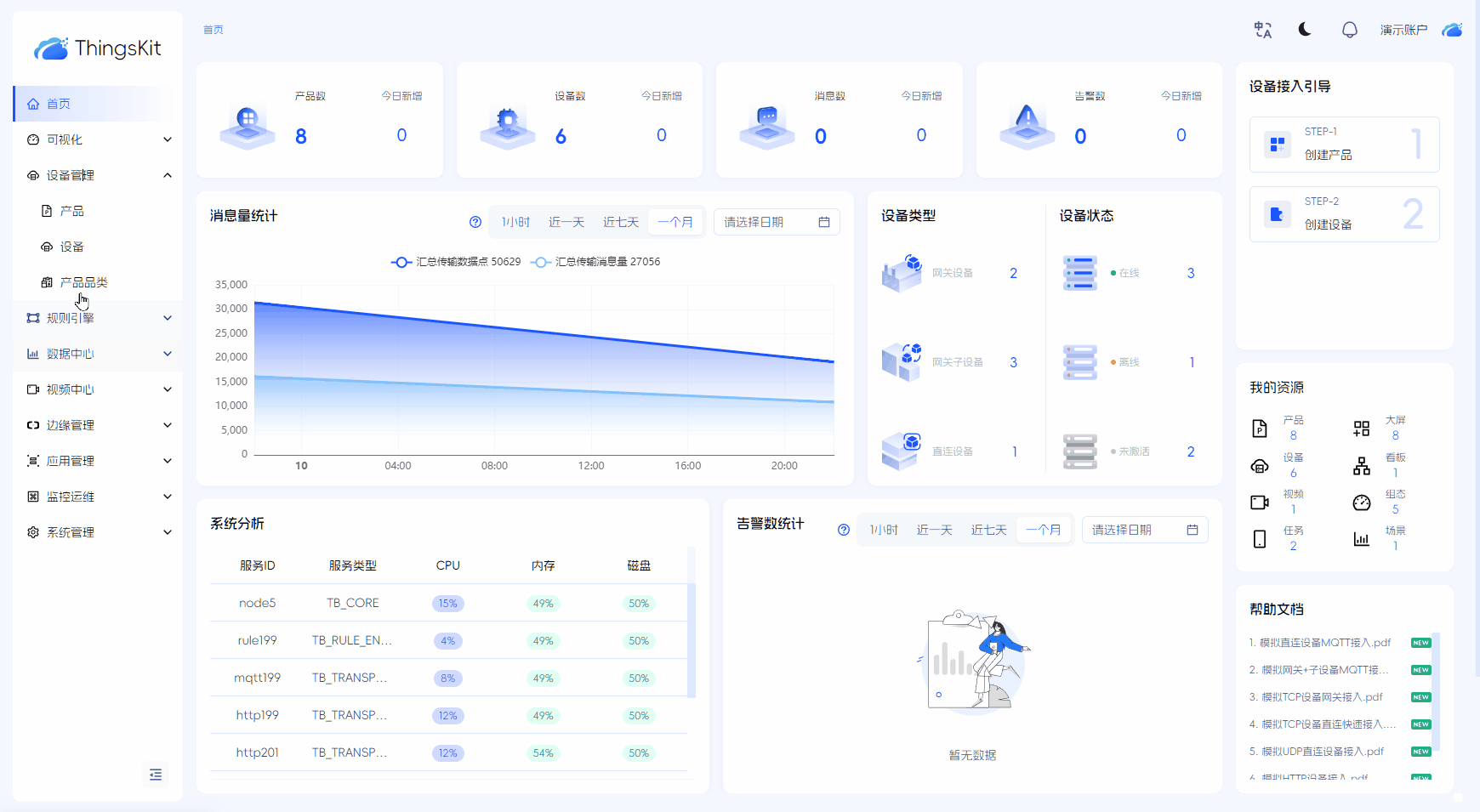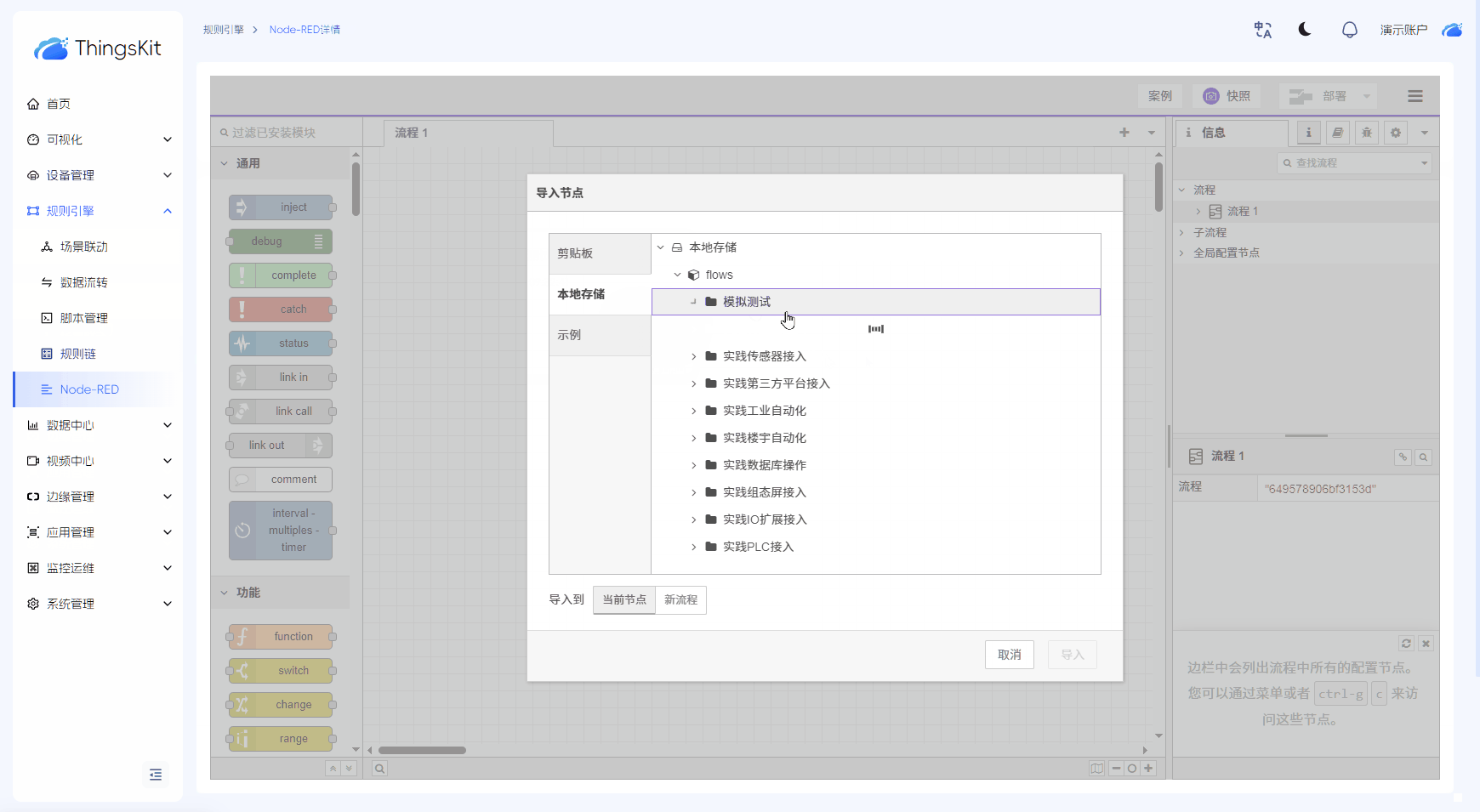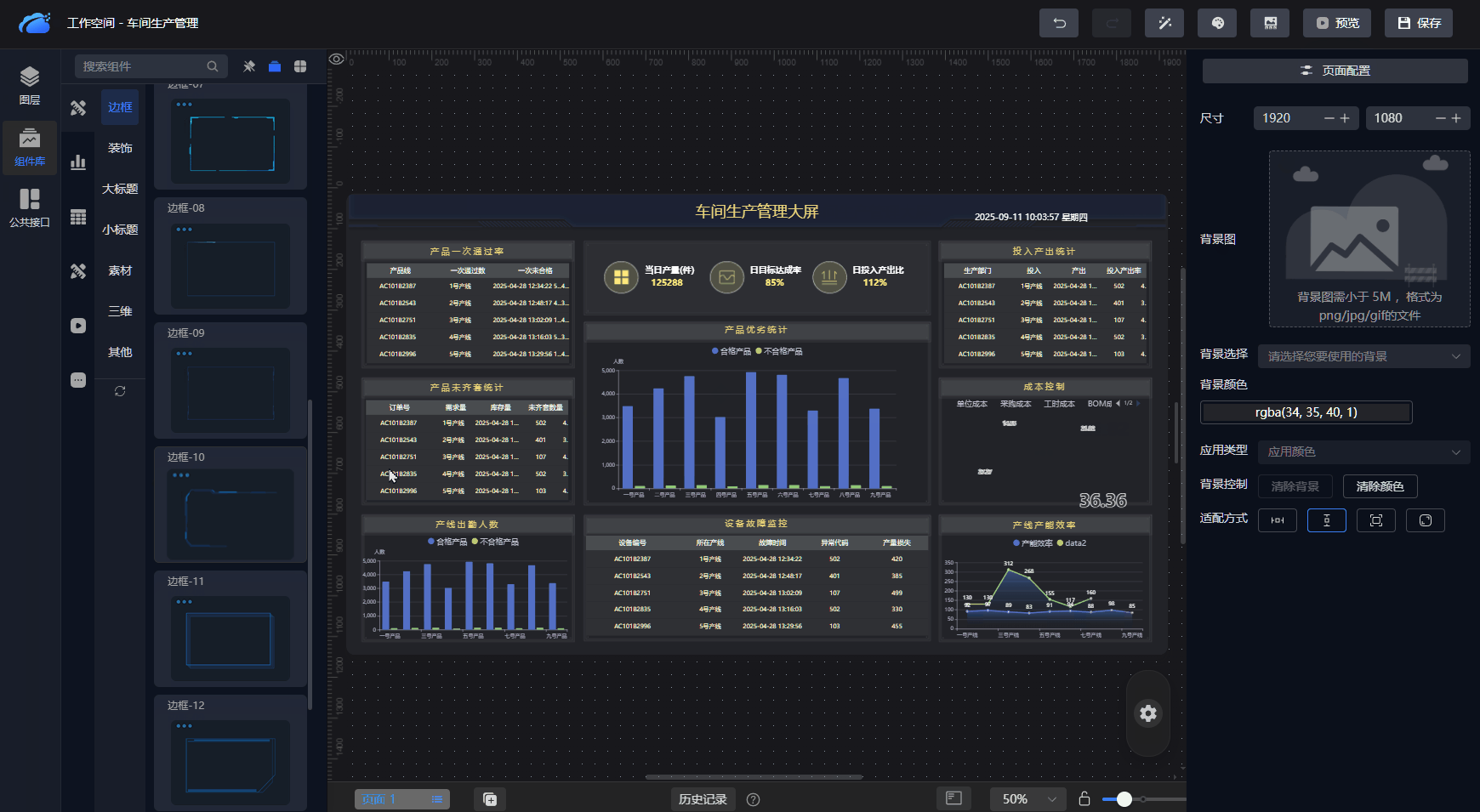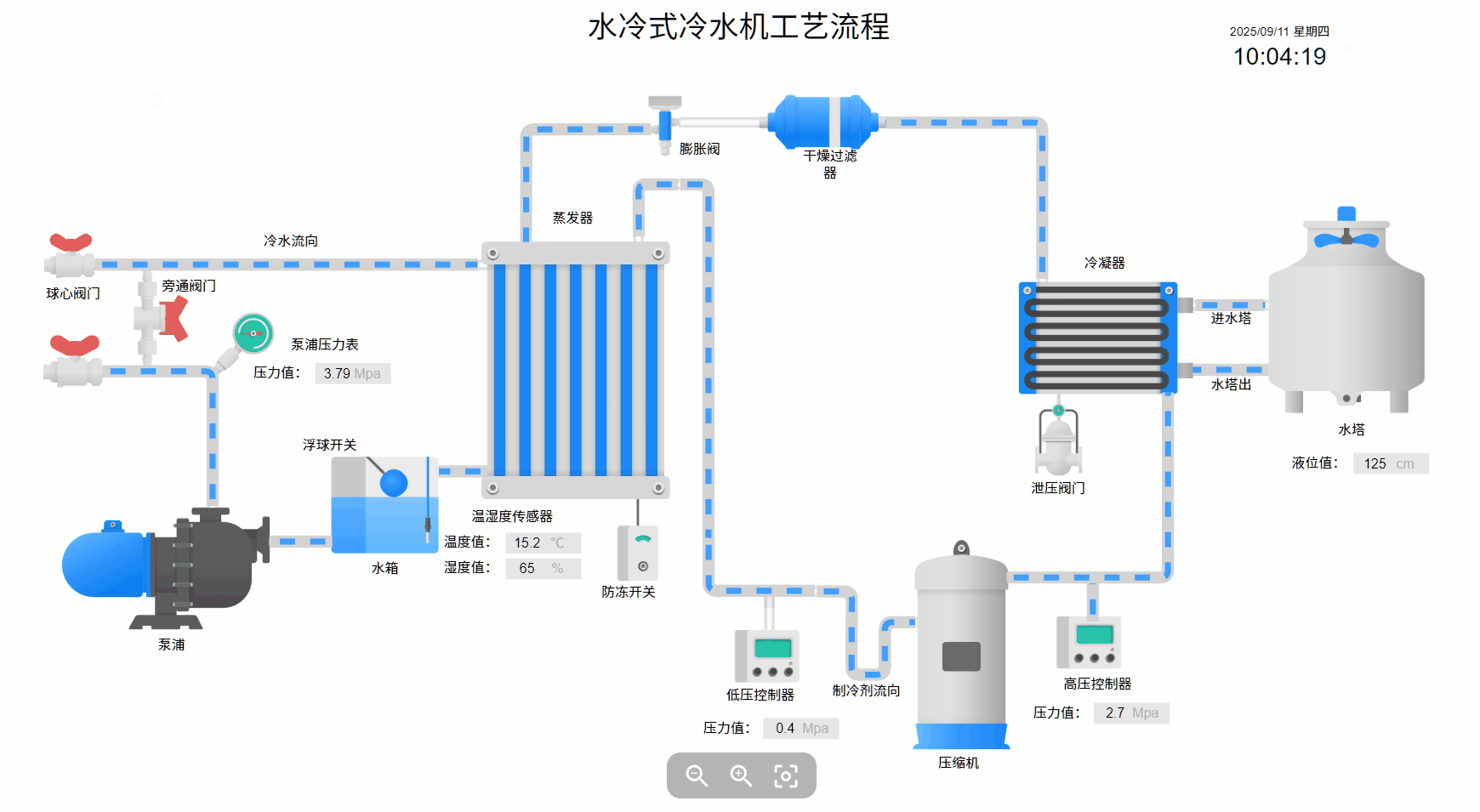
设备接入与管理
通过行业标准物联网协议(MQTT、TCP、CoAP)连接设备,并提供完善的设备管理功能。
云边协同
将物联网云平台上的规则节点、设备、组态、模型、租户信息等资源无缝同步给边缘平台。
数据可视化
采用低代码开发模式,通过拖拽设计可视化大屏、组态,快速实现物联网数据可视化。
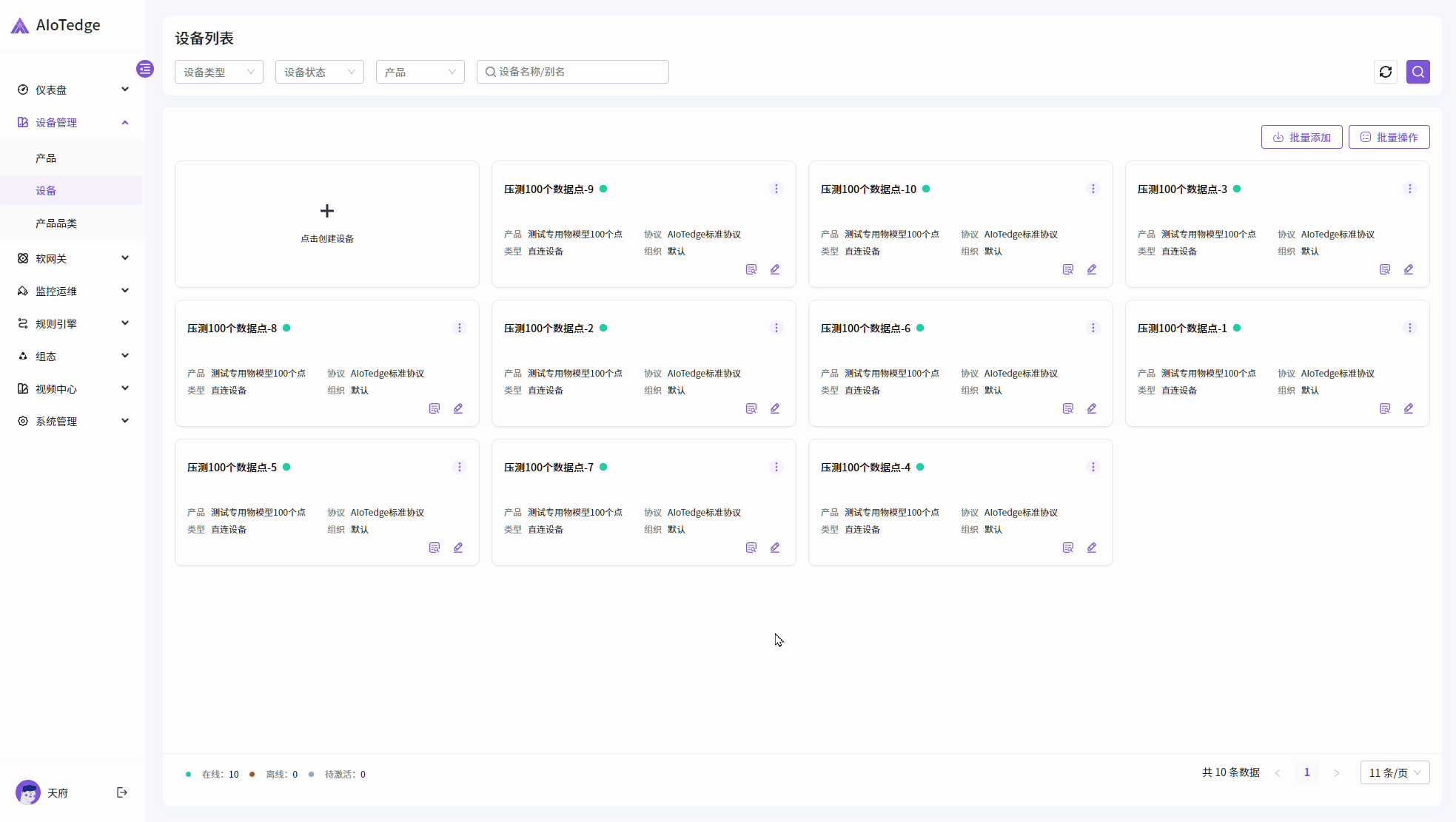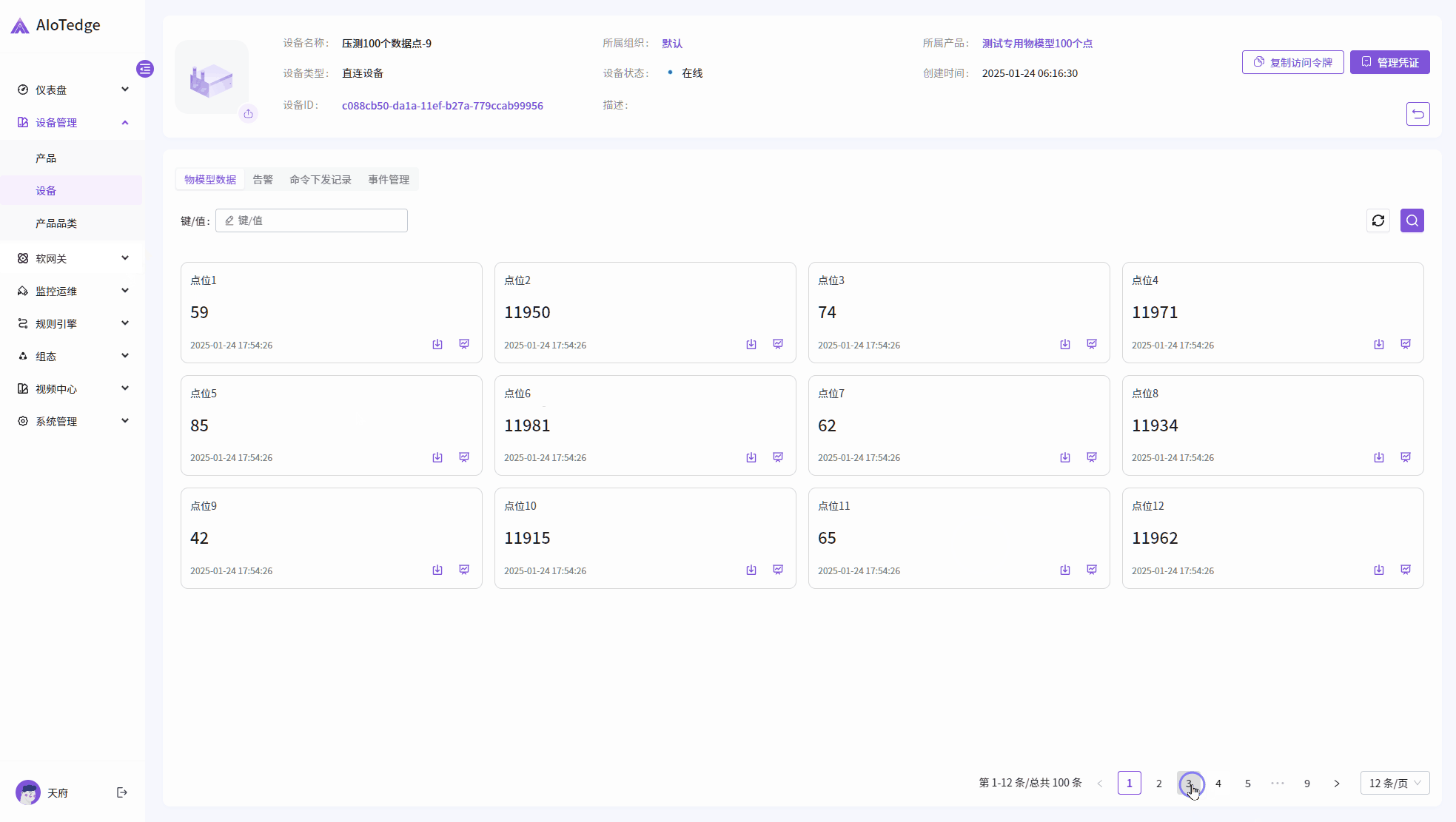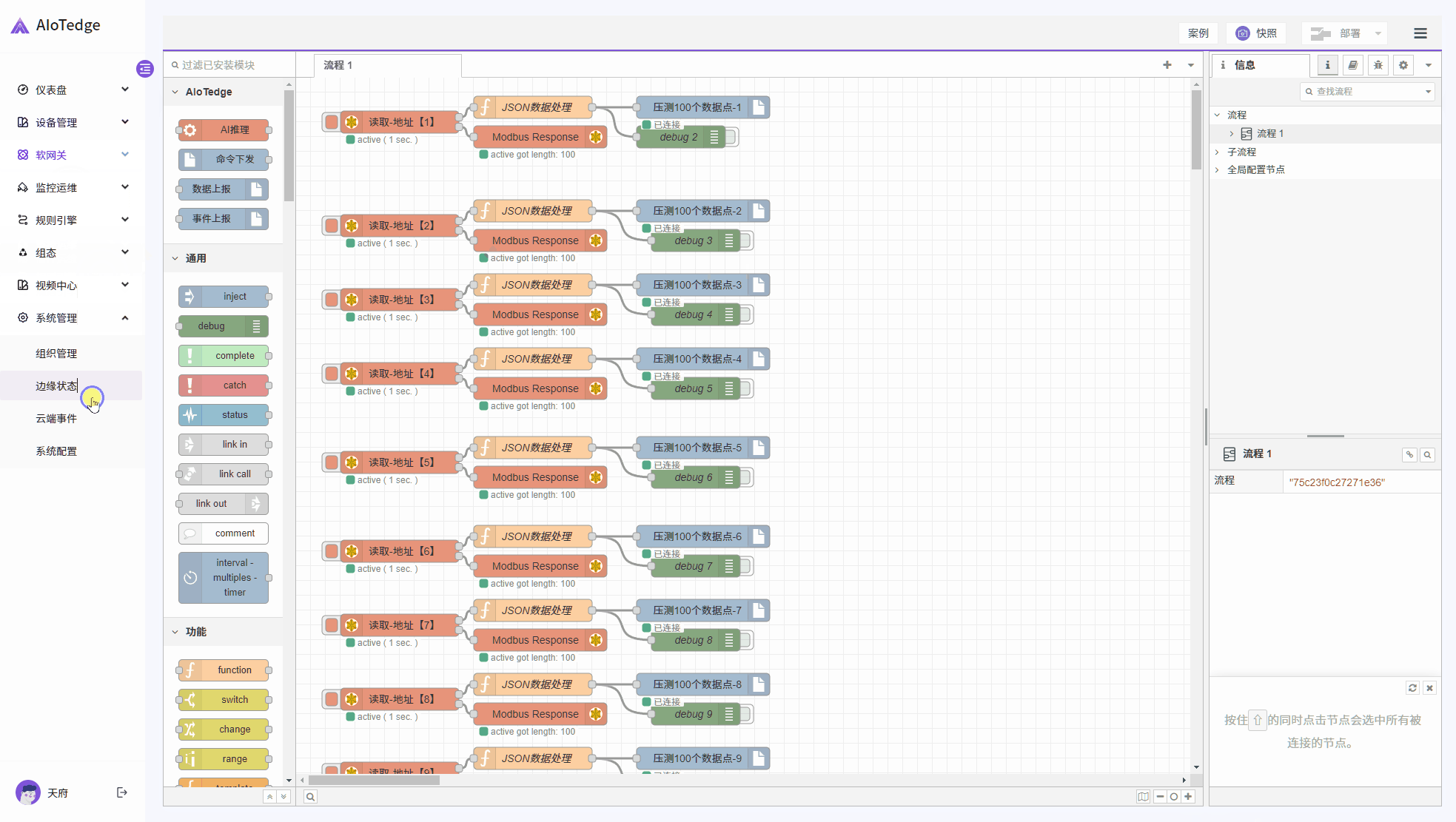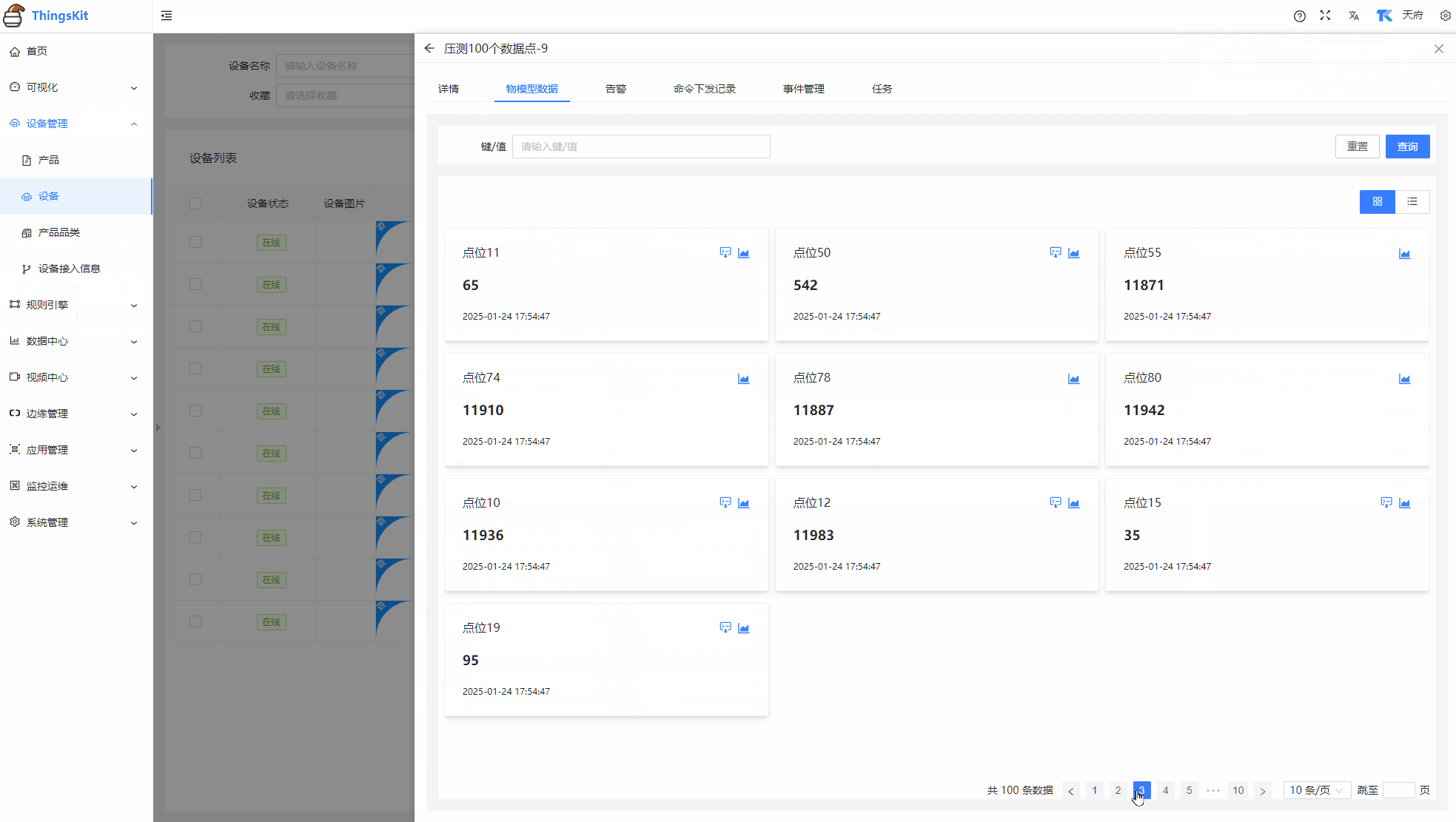
规则引擎
支持可视化配置规则引擎与NodeRED流式编程,灵活适配多场景需求,高效处理IoT数据。